The study on “Antiadhesive Effects of Xylitol on Otopathogenic Bacteria” was completed by Tero Kontiokar, Matti Uhari, and Markku Koskela from the Department of Paediatrics and Division of Microbiology at the University of Oulu, Finland.
In an earlier study the researchers found that xylitol was effective in preventing acute otitis media in children. Other studies have shown that xylitol inhibits the adhesion of cariogenic Steptococcus mutans. For this study the researchers hypothesized that xylitol may also affect the adhesion of otopathogens, therefore they tested this hypothesis in vitro.
Below is the abstract of their study.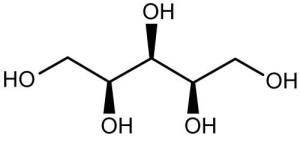
“The exposure of either epithelial cells or pneumococci or both to 5% xylitol reduced the adherence of pneumococci. Exposure of epithelial cells or bacteria alone to xylitol did not reduce the adherence of Haemophilus influenzae, although the exposure of both cells and bacteria to xylitol reduced the adherence significantly. The adherence of Moraxella catarrhalis remained low irrespective of the exposure.” [What this study suggests is that xylitol interferes with how these bacteria hold on to us, and if they can’t hold on they are washed away by the body’s normal cleaning processes. That is a win-win situation because these bacteria that are washed away are not there to develop resistance, which is one of the biggest problems we have with the use of antibiotics. Xylitol can be a help in coping with upper respiratory infections of all types.]
Visit the US National Library of Medicine National Institutes of Health to read their abstract and find the link to the full study.




